The Migrant Project
Project 1:
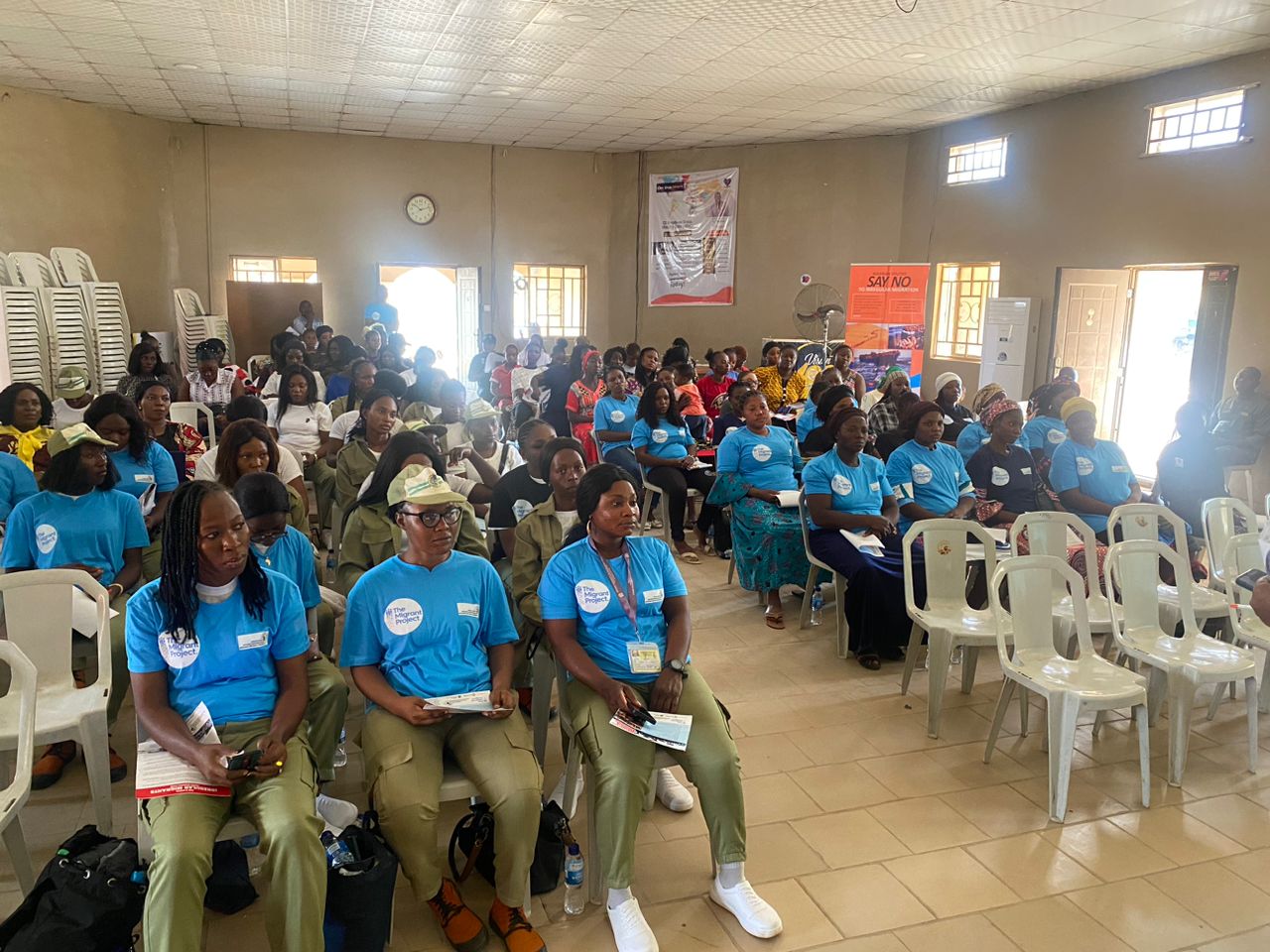
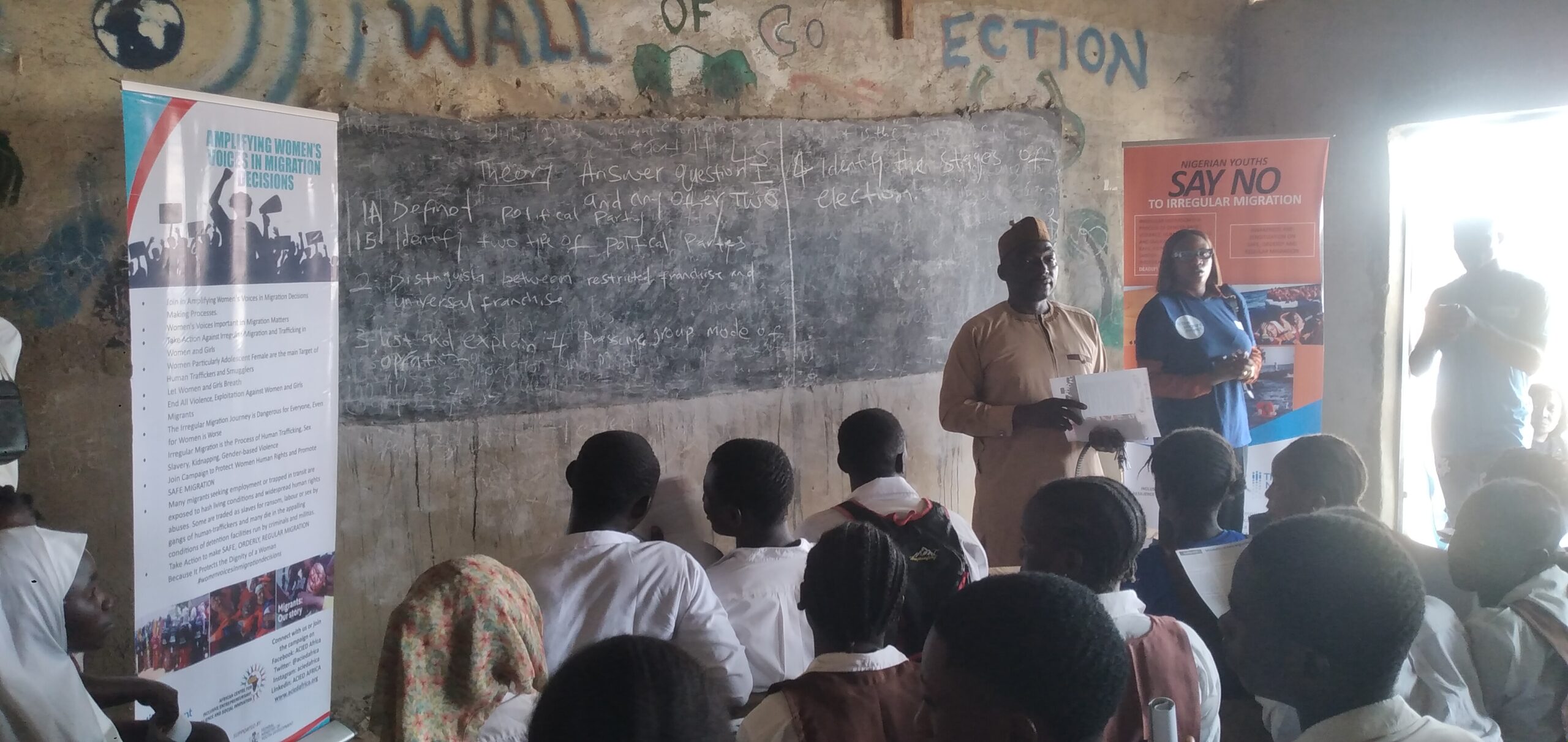
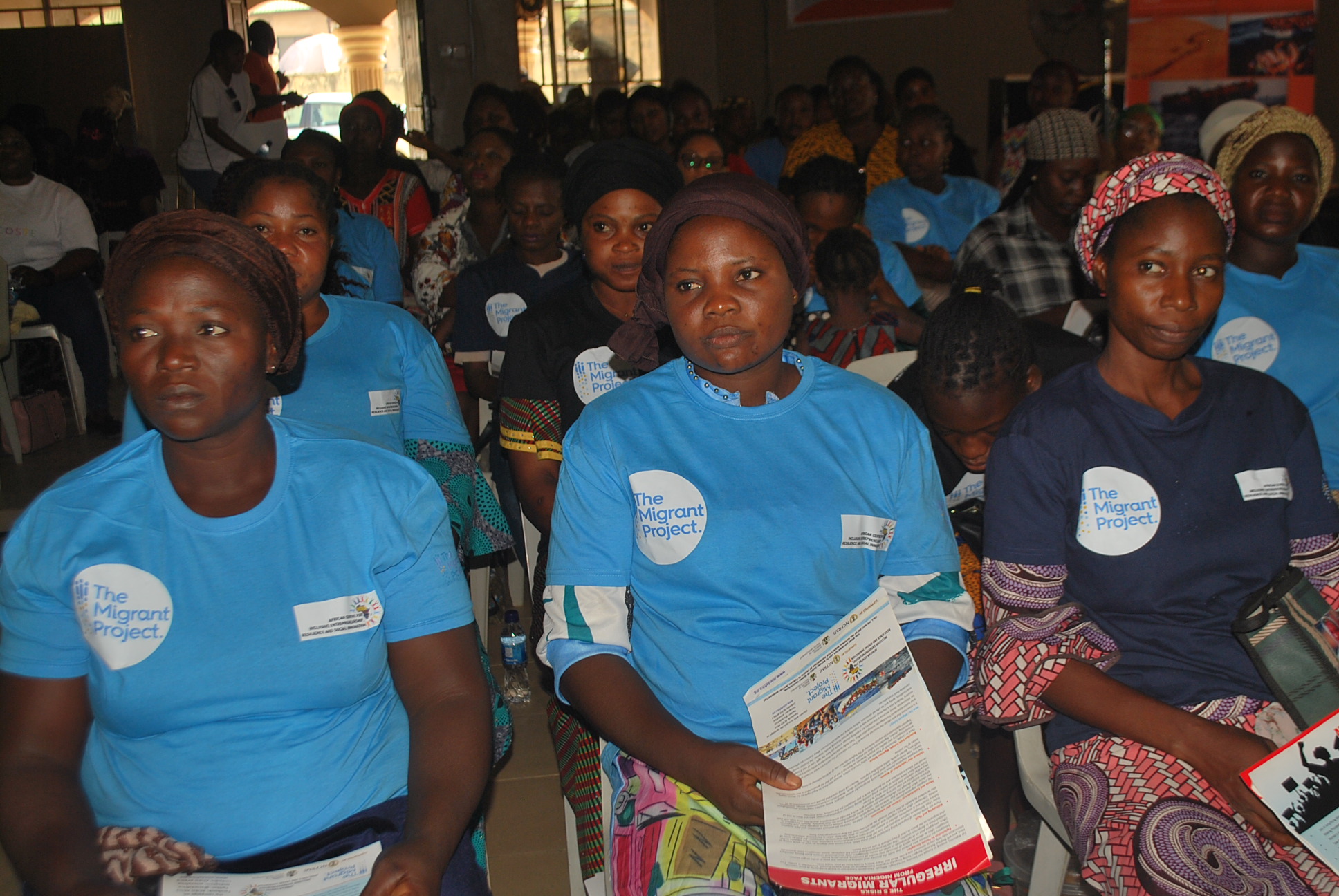
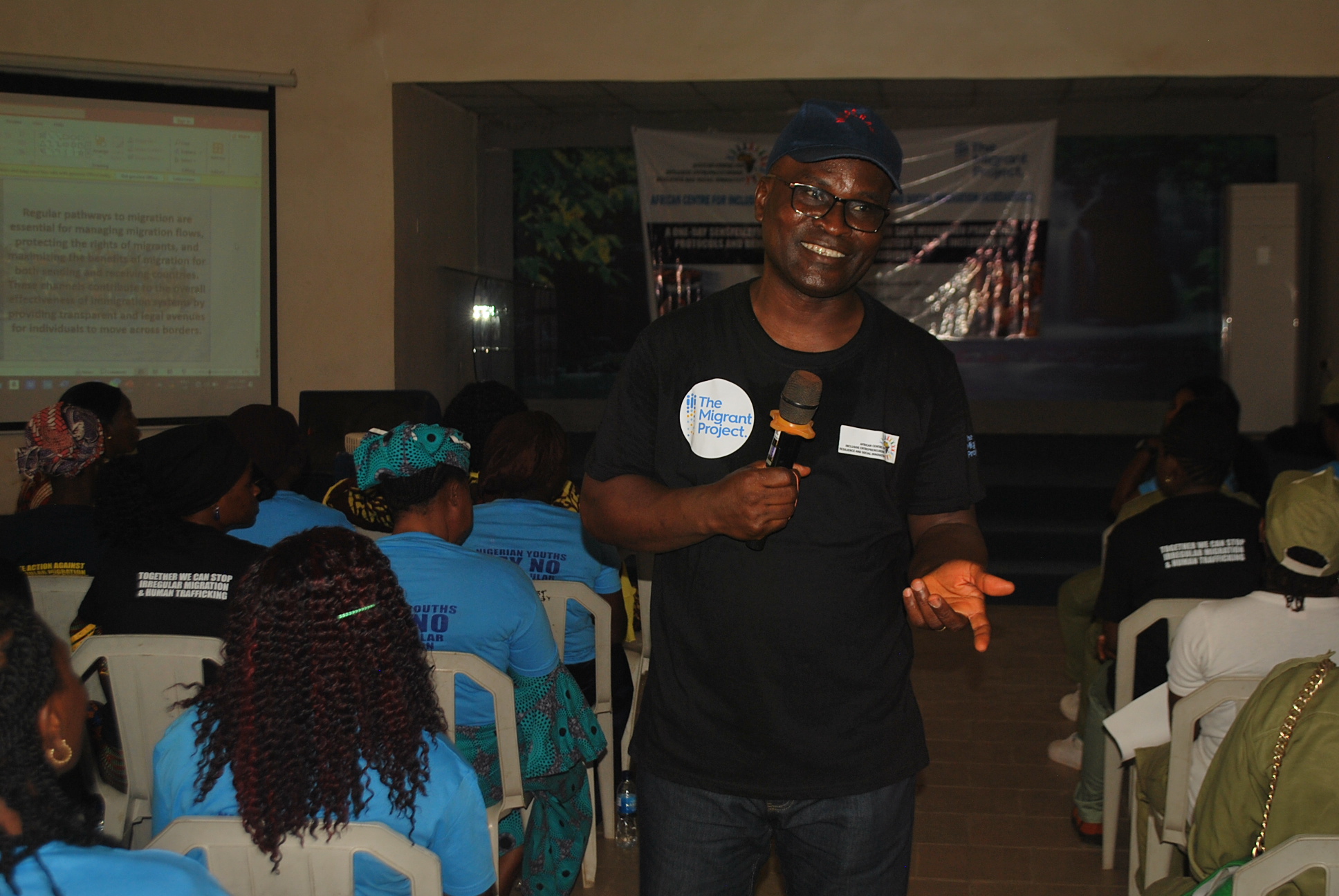
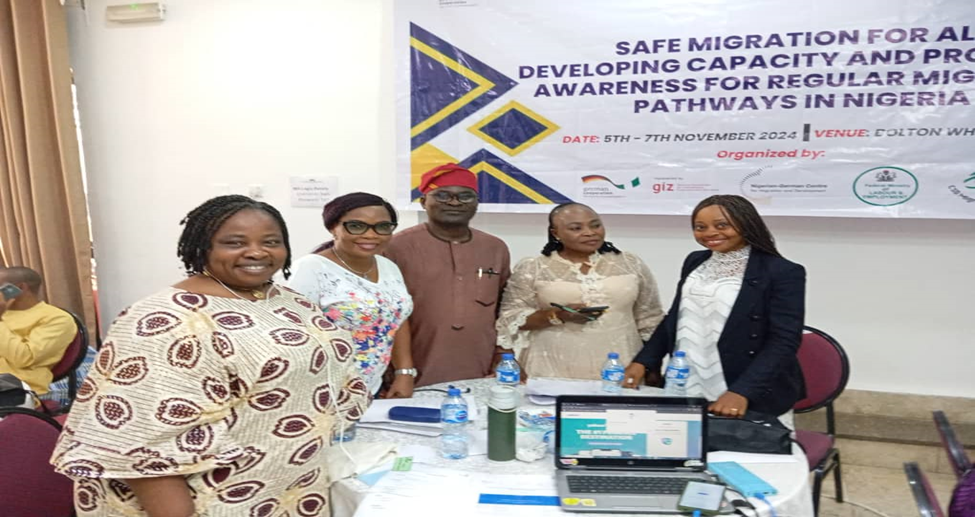
“Strengthening Voices of Women in Migration Decisions Making: Developing Capacity on Regular Migration Pathways in Nigeria and Promoting Awareness
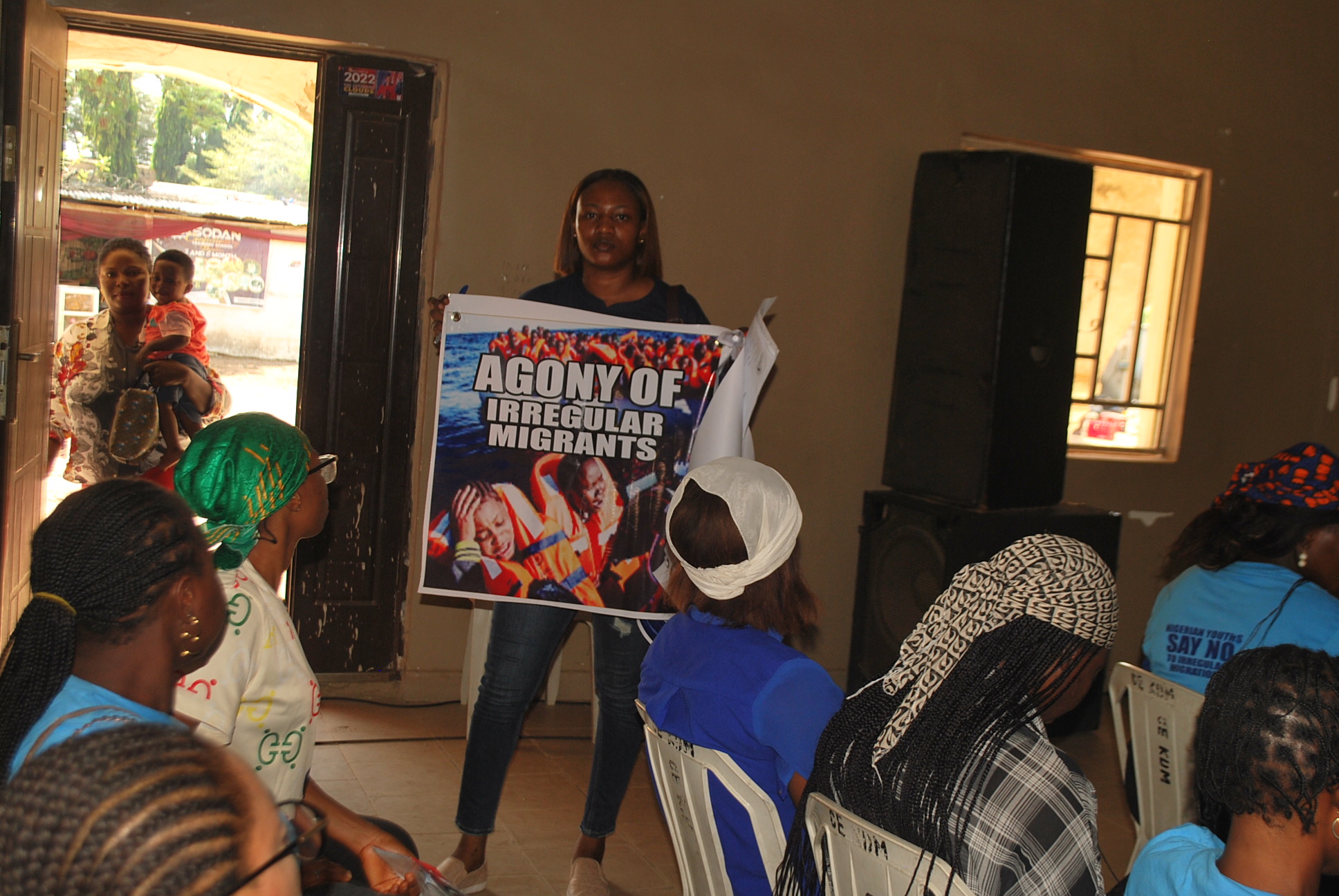
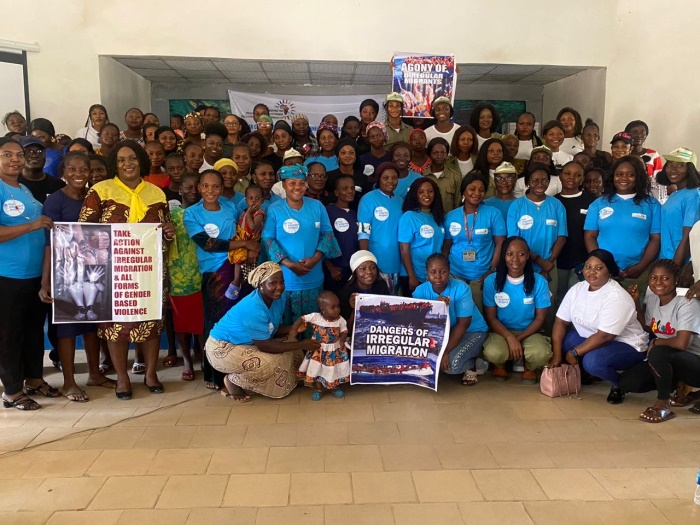
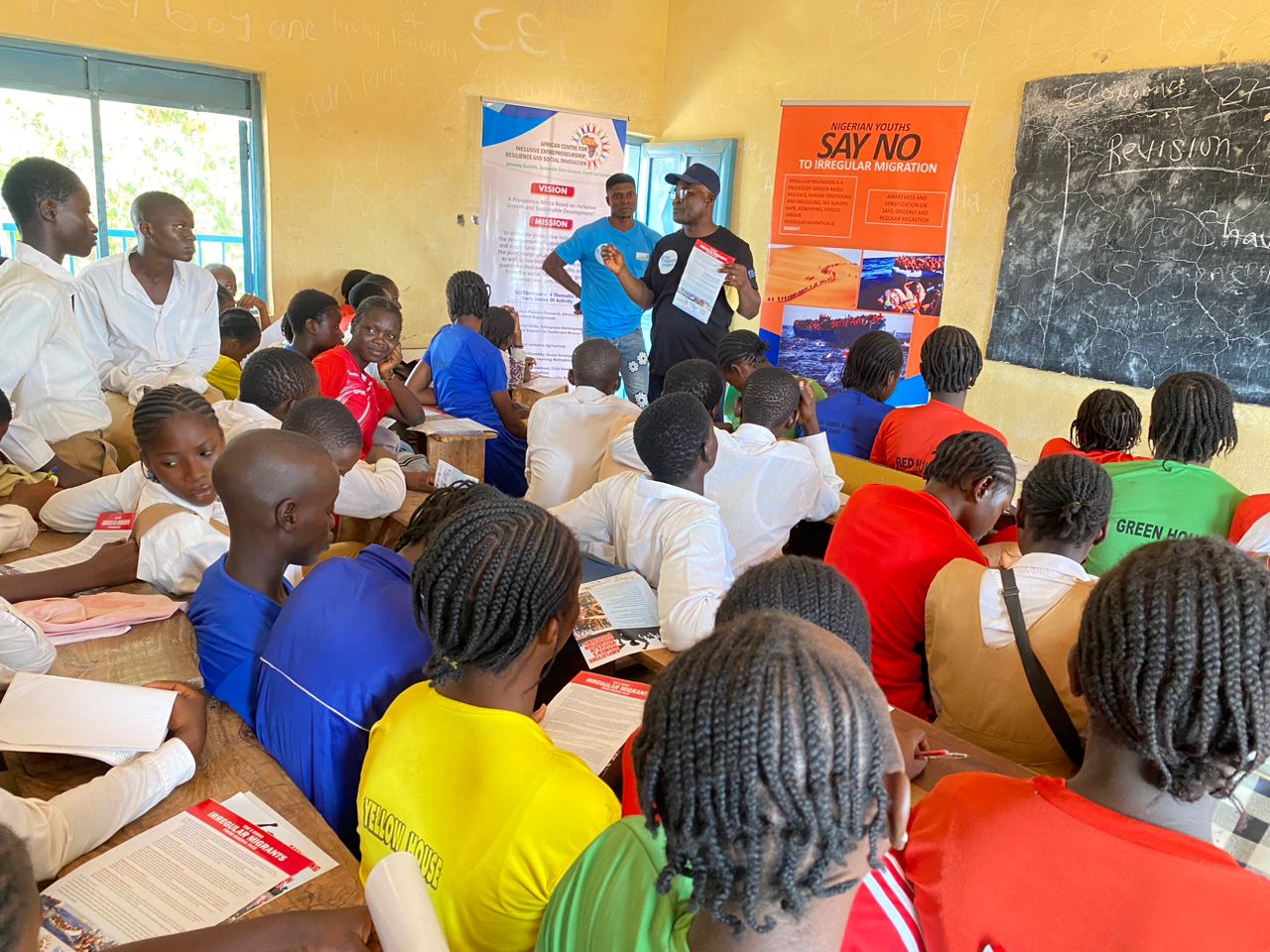
The scourge of irregular migration has become an impediment to the effective management of
migration, and has resulted in the loss of lives of many, lack of knowledge the whereabouts of
some others, trafficking in persons (TIP), smuggling of migrants (SOM), detention by authorities
and other rights violations, as well as risks associated with the hazards of the journey, especially
over land and seas and other consequences of irregular movement. International Organization
for Migration (IOM) has stated that 48 percent of refugees and displaced persons are women,
who are increasingly autonomous in their migratory processes. It has alerted that women are
impacted by discrimination and violence in all stages of migration because of their gender,
ethnicity, or migratory status, among others. Moreover, there are numerous sociopolitical
barriers that limit the participation of migrant women in influencing policy-making spaces, and
their “needs, priorities and voices are often missing from policies designed to protect and assist
them. Despite the high mobility of people in and out of Nigeria, migration is often undertaken
under risky circumstances as migrants often receive little or no adequate information about
their fundamental human rights, legal migration processes and the risks inherent in irregular
migration. Through access to reliable and objective information on migration, migrants will be
able to make informed decisions about their migration route and mitigate the risks associated
with irregular migration.
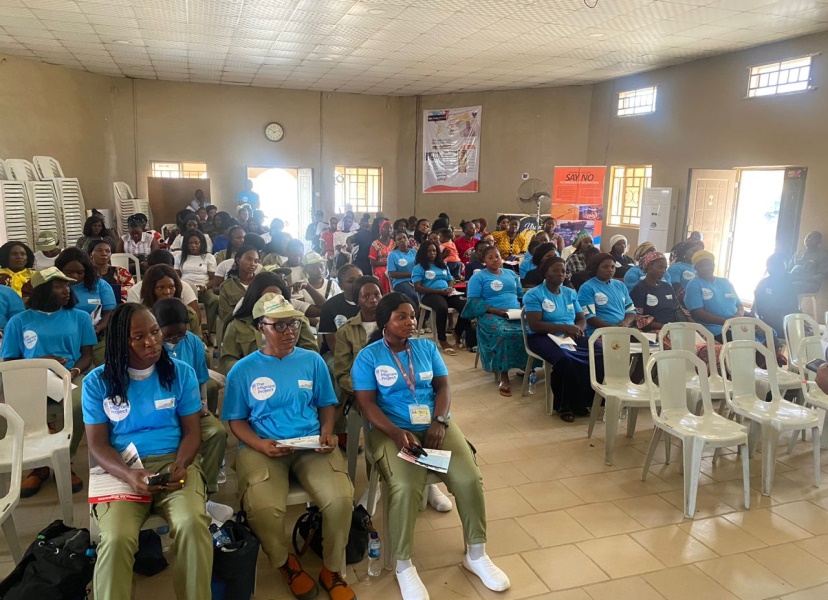
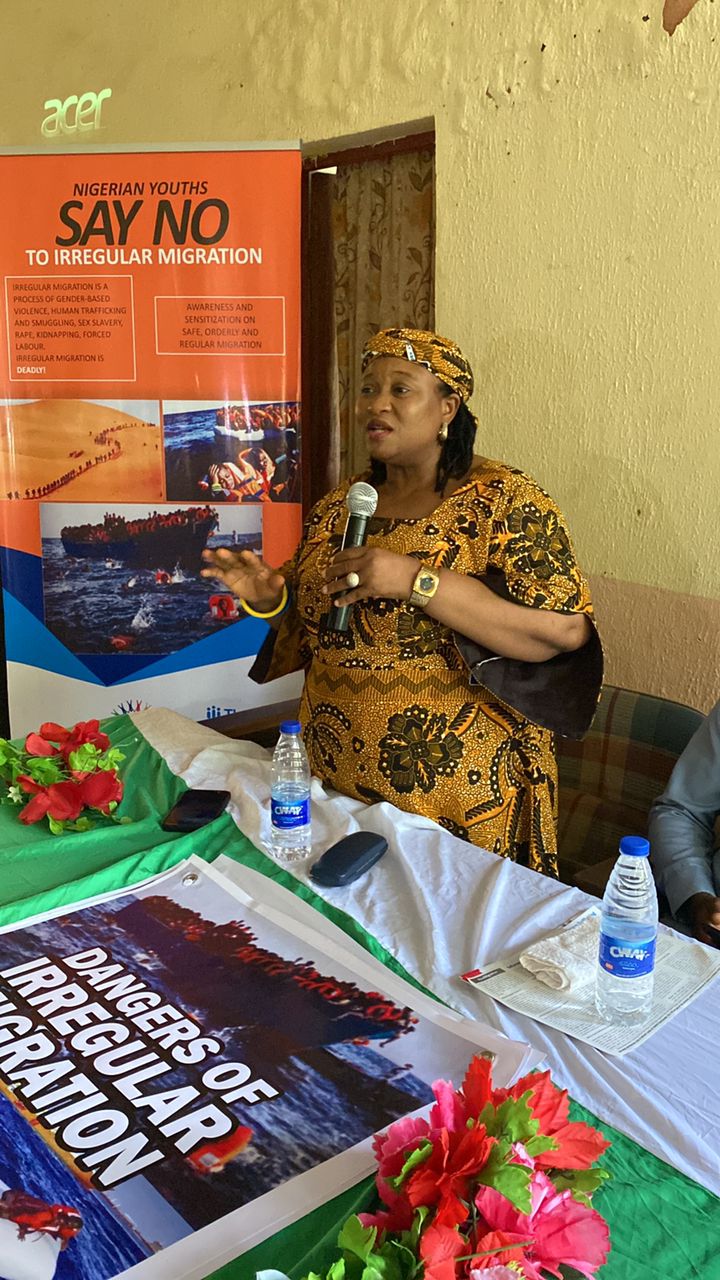
To address the scourge, ACIED Africa through “The Migrant Project” has been implementing an
Effective Migration Communication Campaign Leveraging Innovative Technologies For
Strengthening Women and Youth’s Voices In Migration Decisions In Nigeria. This is to help a
massive number of young people particular females in Nigeria with knowledge and behaviours
that reduce investment in risky migration, as well as increase the influence of women on their
societies’ norms around irregular migration.
Specific Objectives for Promoting Safe and Regular Migration Pathways
- Increased Use of Regular Migration Pathways:
Facilitate informed decision-making based on accurate and up-to-date information about regular migration channels, leading to a higher adoption of safe and legal migration routes. - Empowerment of Nigerian Youth and Workers:
Equip Nigerian youth, particularly young females, with the knowledge and skills to actively participate in promoting safe migration practices and advocating for the rights of migrants within their communities. - Systemic Change and Inclusive Policy Design:
Influence systemic change to ensure the inclusion of women and disadvantaged groups in the design and implementation processes of migration policies. - Strengthened Youth-Led Platforms:
Support and enhance youth-led initiatives and platforms that advocate for and promote safe migration pathways across Nigeria. - Addressing Root Causes of Irregular Migration:
Advocate for policies and initiatives that address the underlying causes of irregular migration by creating an enabling environment for youth to pursue safe and regular migration opportunities. - Enhanced Regional and International Engagement:
Increase advocacy and engagement with Nigeria, the European Union (EU), and ECOWAS to collaboratively implement common approaches and actions for promoting safe migration pathways and controlling irregular migration and human trafficking, particularly of women and children, within ECOWAS migration corridors.
Project 2:
Innovative Transformation of Rural Enterprises and Community Resilience Programme (T-CORE)
The ACIED Africa’s T-CORE flagship initiative aims at rural transformation through strategies that
focuses beyond poverty alleviation by building sustainability, resilience and prosperity of rural
communities through innovative digital enterprise promotion, access to finance and employment
opportunities.
Components of the T-CORE
1. Rural Enterprise Ecosystem Development
The main objective of this component is to create an enabling rural business development ecosystem. ACIED Africa undertakes the following activities:- Diagnostic Studies: Conducting community analysis, value chain analysis, and sector/sub-sector identification.
- Identifying Potential Enterprises: Using participatory methods to promote rural enterprises for both groups and individuals.
- Strengthening Existing Rural Enterprises: Identifying market and value chain development opportunities.
- Providing Business Development Support: Offering informed pathways to develop sustainable businesses with a primary focus on promoting women and youth-led enterprises and green enterprises.
2. Enterprise Business Plans Financing and Innovations
This component aims to bridge the demand–supply gap for new and group enterprises to access finance from formal financial institutions. It envisions building a good credit history and sustainable relationships between the promoted enterprises and financial institutions, ensuring long-term financial linkages. The innovation promotion aspect contributes to the design, promotion, and implementation of transformational and innovative ideas that use technology, innovation, and partnerships to tackle development challenges. ACIED Africa views innovation as an Idea for Change, which could enhance business practices, efficiency, processes, new product development, improved crop cycles, reduction in GHGs, and drudgery reduction. Key features of innovation under this component include:- Applicability: Relevance to the context of rural livelihoods.
- Replicability: Demonstrated potential in other locations.
- Scalability: Expandable in terms of geography and human coverage.
- Sustainability: Ability to be maintained without external support.
- Impact and Outcomes: Long-term social, economic, and environmental benefits.
3. Skills and Job Opportunities
a. Enhanced Employment Outcome
This sub-component enhances access to services and employment outcomes for youth, women, and persons with disabilities from poor households by providing training through existing flagship government skills training programs. Key activities include:- Providing pre- and post-training services, including identifying and mobilizing target youth.
- Developing information packs on training types and schedules.
- Offering pre-training counseling services to help youth interpret available information and make optimal training choices.
- Providing post-training support, including counseling, emergency assistance, and access to basic services in destination areas.
b. Community-Based Training and Skilling Provision
This sub-component enhances the access of target households to skills training in locally relevant sub-sectors. It supports Community Skills Schools (CSSs) and Community Farm Schools (CFSs), with local experts capacitated through the project to deliver village-level training services. This approach enables women, youth, and persons with disabilities to access such training. Additionally, the project supports outreach with local MSMEs and entrepreneurs to identify market needs and facilitate post-training placement and employment. By addressing the productivity gap in both on-farm and off-farm activities, this component aims to improve agricultural productivity and promote off-farm rural employment through the acquisition of modern practices.c. Entrepreneurship Development Programme
The Entrepreneurship Development Programme (EDP) equips entrepreneurs and Lead Farmers with enhanced entrepreneurial skills across various aspects, including finance, marketing, business plan preparation, convergence with other schemes, and legal compliance.Project 3:
Youth Entrepreneurship and Employment Support
When the youths are empowered with entrepreneurial skills and are able to set up functional
businesses and create jobs, the rate of poverty in the country would be reduced likewise the
level of criminality. Available data show that agriculture has been the highest employer of
labour in Nigeria and has been demonstrated to be an effective means to lift groups out of
poverty. Agriculture has the potential of absorbing the massive unemployed and
underemployed youth population to make them contribute meaningfully to economic growth
and national development.
To enhance the labour supply, the rural youth need access to entrepreneurship education and
training in order to develop job-relevant skills for agriculture and non-farm occupations,
increasing their productivity and employability. Better educated youth in entrepreneurship will
have the skills to start a business, help them see agriculture as a viable livelihood option, and
are more likely to make good use of resources and adopt innovative agricultural technologies.
These skills can be developed through Entrepreneurship Education, Technical and Vocational
Education and Trainings (TVET) systems, skills development programmes.
Youth Entrepreneurship and Employment Support (YES) Initiative
The Youth Entrepreneurship and Employment Support (YES) is one of the flagship programmes conceptualized under the principles of community-based training to promote innovation, income generation and economic empowerment of the rural poor. YES initiative is meant to create opportunities for the rural youth to build their economic livelihoods through rural entrepreneurship or employment. It also aims to increase their engagement in the rural sector, contribute to sustainable rural transformation, and develop a new generation of young farmers, agripreneurs and rural supply chain actors.Key Outcomes
The key outcomes are:- Young people acquire skills enabling them to take advantage of employment and business opportunities.
- Young smallholder farmers, rural entrepreneurs and SMEs have access to markets and services.
- Young smallholder farmers, rural entrepreneurs, and migrants and their families have access to financial products and services to finance their businesses.
Strategic Focus
In order to most effectively achieve its aim of attracting young millennials to participate, YES needs to focus on:- Innovation: Leveraging technology and modernizing agricultural employment and practices.
- Incentives: Creating incentives for young people for rural entrepreneurship.
Programme Components
The YES activities are grouped into four interlinked and complementary components:- Rural Youth Transition to Work:
- Facilitating the transition of rural youth into employment.
- Rural Youth Entrepreneurship:
- Building the rural youth skills and business development services.
- Creating employment opportunities.
- Investing for Rural Youth:
- Linking capacitated youth to financial institutions.
- Providing initial investments for young entrepreneurs.
- Enabling Environment for Rural Youth:
- Developing evidence-based influencing strategies to engage Nigeria government at all levels.
- Advocating effective policy actions that create enabling environment for the youth businesses to strive.
HOW WE MAINSTREAM GENDER INTO OUR AREAS OF WORK
-
Climate Change and Agriculture
Women play a critical role in agriculture, contributing significantly to food production, rural livelihoods, and sustainable development. Nevertheless, they are often limited in terms of resource ownership and decision-making power. Similarly, climate change disproportionately affects women and girls due to gender roles and differences in rights and responsibilities, decision-making, incomes, and more. These circumstances also exacerbate pre-existing inequalities, vulnerabilities, and poverty. As a result, women are often less able to adapt to climate change than men. ACIED Africa’s climate change and agriculture work utilizes gender-responsive and gender-transformative approaches, fosters equitable opportunities, and promotes the leadership and agency of women within the agricultural sector. By integrating a gender lens into our agricultural programs and initiatives, we empower women to participate actively in and benefit from agricultural value chains while working with communities to support these positive changes. ACIED Africa’s Sustainable and Inclusive Agriculture is a multi-faceted, holistic approach to working with and supporting small-scale farmers to sustainably improve agricultural production and productivity, as well as to build their resilience to external shocks and the effects of climate change.Our Specific Actions to Foster Greater Equality and Empowerment
a. Gender Analysis
- Examine climate change and agriculture from a gender perspective, to understand what men and women are doing, how they are affected by climate change, and how different approaches can work better for them.
- Examine gender preferences regarding times, locations, equipment, and practices to ensure accessibility and availability for women to participate in project activities.
- Address the underlying causes of vulnerability for women – including poverty, poor governance, environmental degradation, unequal access and control over resources, limited access to basic services, and gender inequality – and ensure that the project responds to these circumstances.
b. Education and Economic Empowerment
- Provide adult literacy training, including financial literacy, to support women’s market access.
- Promote women’s equitable access to agricultural inputs (like crops, natural pesticides, fertilizer, and equipment) and land.
- Support women to establish local savings and lending groups.
- Ensure all communication and training provisions are gender-sensitive and take into account women’s needs and preferences (communication can, for example, be face-to-face, via SMS, and more).
- Promote climate-resilient livelihoods and build resilience capacity for women.
c. Inclusion in Decision-making
- Support women to get necessary paperwork to strengthen their access to public/legal services and rights.
- Promote women’s leadership on local agriculture committees/groups and on climate action, and encourage men to support women in such leadership roles.
- Value women’s expertise and knowledge to complement newer practices.
d. Awareness Raising
- Lobby for gender-sensitive and gender-transformative policy and mitigation measures.
- Work with communities to raise their awareness of and support for women active in income generation, decision-making, and agricultural value chains.
- Raise awareness among women and men about climate change and its different impacts on\n different community members.
QUICK LINKS
PROJECTS
4 THEMATICS
ALL CONTACTS
- Suite C-034 H&A Plaza, along Olusegun Obasanjo Way, Wuye District Abuja-Federal Capital Territory, Nigeria
- +234 906 202 2245
- info@aciedafrica.org, aciedafrica.ng@gmail.com
- Copyright © 2025 ACIEDafrica. All Rights Reserved.